Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
The aliquot of an extract of malt is added to a buffered starch solution and allowed to stand for exactly 30 min at 20 °C. Then, the maltose – formed primarily from the starch through the action of the β-amylase – is measured using iodine and is determined according to the following chemical reaction:
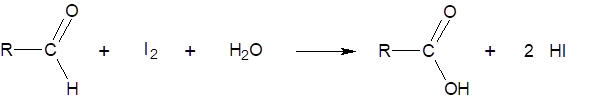
Determination of the percentage of nitrogen that has dissolved in the wort during the Congress mash method
Suitable for (Congress) mash
The Kolbach index is used to express the quantity of the nitrogenous substances found in malt, which go into solution under the conditions present during the Congress mash method. It is a measure of the degree of proteolytic modification of the malt and also provides an indication for the quantity of proteolytic enzymes contained in the malt. The Kolbach index is less conclusive than other methods due to its dependence on the total nitrogen content and the provenance of the barley. Therefore, it must always be considered together with the total nitrogen content.
Potassium permanganate oxidizes many organic and certain inorganic substances more or less completely in acidic, neutral or alkaline solutions. The volume of potassium permanganate required in the analysis is determined potentiometrically. Since oxidation depends on the type of solution, on its temperature and on the reaction time, the procedure described below must be followed precisely.
In acidic solutions, permanganate ions are typically reduced to manganese(II) ions:
MnO4- + 5 e- + 8 H3O+ → Mn2+ + 12 H2O
In alkaline solutions, the reduction results in tetravalent manganese only:
MnO4- + 3 e- + 4 H3O+ → MnO2 + 6 H2O
Since in both cases the titration takes place in an acidic solution, this is irrelevant for the calculation. By adding oxalic acid, both the excess permanganate ions as well as the tetravalent manganese are reduced to manganese(II) ions:
2 MnO4- + 5 C2O42- + 16 H3O+ → 2 Mn2+ + 24 H2O + 10 CO2
MnO2 + C2O42- + 4 H3O+ → Mn2+ + 6 H2O + 2 CO2
Barley intended for the production of malt is evaluated on the basis of germinative capacity.
This method is used to determine the percentage of germination that will occur under normal malting conditions. The germination index provides a good indication of the germination capacity of a barley lot which is no longer dormant [1−3].
The method is based on the BRF/4 ml test with 4 × 100 kernels.
This method describes how to determine the hop storage index (HSI) in hops and hop products.
Hops and hop products intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
The oxidative degradation of the α-acids and β-acids in hops and conventional hop products is determined using a spectrophotometer. The HSI can be referenced in addition to or together with the spectrophotometric method for determining the α-acids and β-acids in hops outlined under R-300.04.110 α- und β-Säuren in Doldenhopfen und Hopfenpellets – Spektralphotometrische Methode.
Applicable for malt (or the wort produced from it) and all (laboratory) worts
The analysis sample (e.g., Congress wort or wort from above the grain bed during lautering) undergoes a chemical reaction with an acetic acid/thiobarbituric acid solution; the resulting product is yellow in color and is measured spectrophotometrically.