This method describes how to determine the moisture content of specialty malt.
Specialty malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
Barley malt (pilsner malt) and smoked malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
The phenol fraction collected through steam distillation is mixed with 4-amino- 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one (4-aminophenazone) under alkaline conditions and oxidized by potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) to form a pigment (fig. 1), which after extraction with chloroform, can be measured spectrophotometrically.
Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
A (modified) Congress wort is produced from malt samples prior to analysis. NDMA present in the Congress wort is extracted using dichloromethane followed by concentration of the eluate. The determination is performed with a gas chromatograph using a packed Carbowax 20M column with a specific TEA detector (thermal energy analyzer); nitrosodipropylamine (NDPA) serves as an internal standard.
This detector analyzes nitrosamine according to the following procedure:
After exiting the GC column, the separated substances are heated to 500 °C in a pyrolyzer. At this temperature, the N-NO bond of the nitrosamine is broken, thus forming an NO radical (NO۰):
The gas mixture then flows through a special filter (CTRTM gas stream filter), which only allows the carrier gas and the NO radicals to pass. After exiting the filter, the NO radicals flow into a reaction chamber along with ozone, which is created by a special generator. The following chemical reactions take place in the chamber:
|
NO• + O3 |
→ |
NO2• |
|
NO2• |
→ |
NO2 + h•ν |
These NO radicals react with ozone, forming nitrogen dioxide in an excited state (NO2•). The NO2• molecules decompose spontaneously to form nitrogen dioxide in its common form (NO2), emitting radiation (h•ν) with a wavelength of approx. 600 nm.
Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
The aliquot of an extract of malt is added to a buffered starch solution and allowed to stand for exactly 30 min at 20 °C. Then, the maltose – formed primarily from the starch through the action of the β-amylase – is measured using iodine and is determined according to the following chemical reaction:
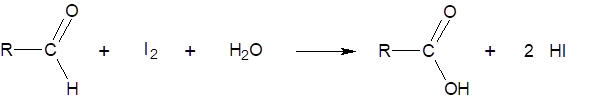
Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
Using a buffer solution, malt extract is produced, and then under defined conditions the extract is incubated on a specific substrate of BPNPG7 oligosaccharide (a p-nitropheny-maltoheptaoside blocked at the non-reducing end) in the presence of thermostable α-glucosidase. The α-glucosidase is initially unable to degrade the "blocked" oligosaccharide. Only when the oligosaccharide is hydrolyzed by the activity of the α-amylase (an endoenzyme) from the malt are the resulting fragments vulnerable to the enzyme. Then, they are quantitatively degraded to glucose and free p-nitrophenol by the α-glucosidase, which is present in excess.
Adding a weakly alkaline solution halts the enzymatic activity and simultaneously induces a color reaction. The absorbance measured at 400 nm is proportional to the activity of α-amylase in the sample.
Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
While α-amylase is active in a gelatinized solution of amylopectin, the viscosity of the solution is constantly dropping due to the degradation of the starch molecules, which can be tracked using a rotational viscometer. The change in the reciprocal of the specific viscosity serves as a measure for the activity of α-amylase.