Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
Using a buffer solution, malt extract is produced, and then under defined conditions the extract is incubated on a specific substrate of PNPβ-G3 (p-nitrophenyl-β-D-maltotrioside) in the presence of highly pure β-glucosidase. The PNPβ-G3 molecule is hydrolyzed through the activity of the β-amylase in the malt to maltose and p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucose. This is cleaved directly to form D-glucose and p-nitrophenol by the β-glucosidase in the substrate mixture. The formation of p-nitrophenol is proportional to the release of maltose by the activity of β-amylase.
Adding an alkaline solution halts the enzymatic activity and simultaneously induces a color reaction. The absorbance measured at 400 nm is directly dependent upon the activity of β-amylase in the sample.
Malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry
The aliquot of an extract of malt is added to a buffered starch solution and allowed to stand for exactly 30 min at 20 °C. Then, the maltose – formed primarily from the starch through the action of the β-amylase – is measured using iodine and is determined according to the following chemical reaction:
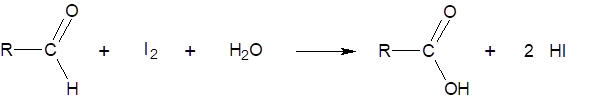
This method describes how to determine the moisture content of specialty malt.
Specialty malt intended for use in beer brewing or elsewhere in the food industry